Quadratic Graphs using x and y axis − 1
Quadratic graphs of the form x2 + bx + c can be drawn by working out where the graph crosses the:
- Y axis − at the number term c in the equation x2 + bx + c
- X axis − by first solving the quadratic so that x2 + bx + c = 0. Refer to
Solve Quadratics by Factorising - 1
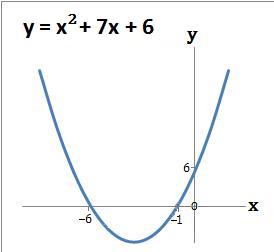
- Example 1. Draw the graph y = x2 + 7x + 6
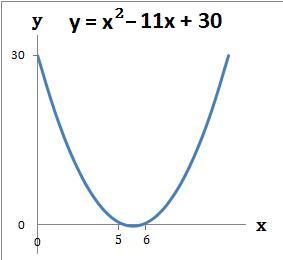
- Example 2. Draw the graph y = x2 − 11x + 30
(a) The graph crosses the y axis at the number term c which is 6. When x = 0 then y = 6. The coordinate is (0, 6)
(b) The graph crosses the x axis where x2 + 7x + 6 = 0. Refer to example 1 of Solve Quadratics by Factorising - 1. So y = 0 when x = −6 or −1. The coordinates are (−6, 0) and (−1, 0)
(c) Draw the graph using the above coordinates
(a) The graph crosses the y axis at the number term c which is 30. When x = 0 then y = 30. The coordinate is (0, 30)
(b) The graph crosses the x axis where x2 − 11x + 30 = 0. Refer to example 2 of Solve Quadratics by Factorising - 1. So y = 0 when x = 5 or 6. The coordinates are (5, 0) and (6, 0)
(c) Draw the graph using the above coordinates